CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS AND ITS CONCEPTS
CLASS 12 ECONOMIC CBSE CHAPTER 1
1.
Describe the five major sectors in an economy according to the
macroeconomic point of view.[3-4 Marks]
Ans: An
economy may be’ divided into different sectors depending on the
nature of study.
Producer sector engaged in the production of goods and services.
2. Household sector engaged in the consumption of goods and services.
Note: Households are taken as the owners of factors of production.The government sector engaged in activities like taxation and subsidies.
Rest of the world sector engaged in exports and imports.
Financial sector (or financial system) engaged in the activity of borrowing and lending.
2.
What are the four factors of production and remunerations to each of
these called? [ 1 Mark]
Ans:
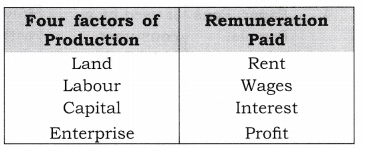
3.
What are the important features of a capitalist economy? [3-4
Marks]
Ans: Features
of capitalist economy are:
Private ownership of land and capital.
Profit is the only motive.
Free play of the market forces of demand and supply.
Government looks after growth, stability and social justice in the economy.
4.
Describe the Great Depression of 1929. [3-4 Marks]
Ans: The
Great Depression took place in 1929 which adversely affected the
developed economies of Europe and North America. It continued for 10
years. There was extreme fall in aggregate demand due to fall in
income, which led to a vicious circle of poverty.
5.
Distinguish between stock and flow. Between net investment and
capital which is a stock and which is a flow? Compare net investment
and capital with flow of water into a tank. [3-4 Marks]
Ans:
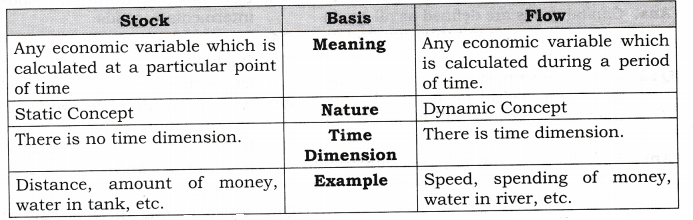
Net
investment is a flow whereas capital is a stock. Amount of water in a
tank at a particular point of time is a stock concept, whereas amount
of water flowing into it is a flow concept.
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED
I.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (1 Mark)
1.
What is meant by circular flow of income?
Ans: It
refers to flow of money income or the flow of goods and services
across different sectors of the economy in a circular form.
2.
What are the three phases of circular flow of income?
Ans: Production
Phase, Distribution Phase and Disposition Phase.
Question
3. Give the meaning of factor income
Ans: Income
earned by factor of production by rendering their productive services
in the production process is known as Factor Income.
4.
What is meant by transfer income?
Ans: Income
received without rendering any productive services is known as
Transfer Income.
5.
Out of factor income and transfer income which one is a unilateral
concept?
Ans: Transfer
incom
6.
Define current transfers.[CBSE 2003]
Ans: Transfers
made from the current income of the payer and added to the current
income of the recipient (who receive) for consumption expenditure are
called current transfers.
7.
Define capital transfers.
Ans: Capital
transfers are defined as transfers in cash and in kind for the
purpose of investment to recipient made out of the wealth or saving
of a donor
8.
What is the meaning of final goods?
Ans: These
are those which are used for:
Personal consumption (like bread purchased by consumer household), or
Investment or capital formation (like building, machinery purchased by a firm)
9.
What is meant by intermediate goods?
Ans: These
are those, which are used for:
Further processing (like sugar used for making sweets), o
Resale in the same year (If car purchased by a car dealer for resale).
10.
What is meant by consumption goods?
Ans: Consumption
goods are those goods which satisfy the wants of consumers directly.
11.
Define capital goods.
Ans: Capital
goods are defined as all goods produced for use in future productive
processes.
12.
Give an example of a person who is staying abroad for a period more
than one year and still he is treated as normal resident of
India.
Ans: An
Indian working in Indian Embassy in the USA will be treated as normal
resident of India.
II.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (1 Mark)
1.
Transfer payments refer to payments which are made:
(a)
Without any exchange of goods and services.
(b)
To workers on transfer from one job to another.
(c)
As compensation to employees.
(d)
None of these
Ans: (a)
2.
Which one of the following items comes under consumption goods?
(a)
Durable goods
(b)
Semi-durable goods
(c)
Non-durable goods
(d)
All of these.
Ans: (d)
3.
Service of a teacher:
(a)
Capital goods
(b)
Consumption goods
(c)
Intermediate goods
(d)
Can be Consumption goods and intermediate goods
Ans: (d)
4.
In a circular flow of income, we have:
(a)
Production (b) Distribution
(c)
Disposition (d) All of them
Ans: (d)
5.
Who is considered as agents of factor
of
production,
(a)
Households
(b)
Government
(c)
Rest of the world
(d)
All of these
Ans: (a)
6.
Which among the following are the
features
of capitalist economy,
(a)
Private ownership of Land and Capital.
(b)
Profit is the only motive.
(c)
Free Play of market forces of demand and supply.
(d)
All of these
Ans: (d)
7.
Flow of Goods & services and factors of production across
different sectors in a barter economy is known as: [CBSE Sample Paper
2016]
(a)
Circular flow (b) Real flow
(c)
Monetary Flow (d) Capital Flow
Ans: (b)
Comments
Post a Comment